What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is the first decentralized digital currency. The management of transactions and the issuance of bitcoins is managed collectively by the Bitcoin network and its users. Therefore, it has no central bank or single administrator. Bitcoin is the first digital-only money. The symbol for bitcoin is BTC or XBT. The pictorial symbol is ₿. Bitcoin is also referred to as a cryptocurrency as it’s transactions are encrypted or protected using cryptography.
Advantages of Bitcoin as a digital currency
Peer to peer transactions
Bitcoins are transferred directly from one person to another. This transfer method is called a peer-to-peer electronic cash system. With regular (fiat) currency, money transfers are done through middle men including your bank, recipient bank, central banks and sometimes intermediary banks.
This has two distinct advantages
Fast
With only two participants, the transfer of bitcoins from one person to another is faster than using the traditional banking system. An average money transfer usually takes 1 – 4 business days while a bitcoin transfer takes less than an hour.
Cheap
The peer to peer transaction removes all the middlemen. Each banking middleman, e.g intermediary bank, payment processor, charges a price for their services and removing them significantly reduces transaction fees for Bitcoin transactions.
Ease of Use – Can be used in every country
Unlike US Dollars, British Pounds or Euros, bitcoins don’t have a geographic region of operation. They can be used everywhere; in any country as long as there is an internet connection.
Your Account Can’t be Frozen
First of all, you don’t have an account with bitcoin. You will have a bitcoin wallet. Since the bitcoin network is decentralized, your account can not be frozen.
No Arbitrary Requirements
Using bitcoins does not require you to fill KYC (know your customer) form. Bitcoins also don’t have any transfer limits. However, maintaining a bitcoin wallet on a regulated cryptocurrency exchange like Coinbase, requires personal disclosures and may have limits on transfers.
History of Bitcoin
Bitcoin as a digital currency was created in January 2009 by an unknown person or group of people named Satoshi Nakamoto. However, on August 18 2008, bitcoin.org was registered to Satoshi Nakamoto, but today, according to Investopedia, the domain is “WhoisGuard Protected”. This means the identity of the person who registered it is not public information. On October 31, 2008, Satoshi released his whitepaper on Bitcoin called “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System“.
A bitcoin is generated or created through a process called bitcoin mining. The first bitcoin block was mined in January 9, 2009. This first block is called the genesis block or Block 0. The following text was added to the genesis block. It reads, “The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks.” It is unknown what the purpose of this text was but it proves that Block 0 was mined on or after that date.
How Bitcoin Works
First off, to use Bitcoins, you need a digital wallet. This is where your bitcoins are stored. Your wallet can be stored on your phone, mobile device, app, computer or a physical bitcoin wallet. A bitcoin wallet is software connected to the bitcoin blockchain that allows you to send, receive and store bitcoins.
Bitcoin Wallets
When you receive cash, you need a place to store them like a wallet or a bank. Your bitcoin wallet works the same way. It is a digital wallet that stores your bitcoins or bitcoin balance. Your bitcoin wallet has your private key, which is like a password to your bitcoin wallet.
There are 2 types of bitcoin wallets. Hot and Cold wallets.
- Hot Wallets
- Mobile or Web Wallets
- Desktop Wallets
- Cold Wallets
Mobile, web and desktop wallets are called hot wallets, while hardware wallets are physical storage devices like flash drives and are called cold wallets.
Mobile or Web wallets
These are the most accessible and convenient bitcoin wallets as your wallet and its private keys are stored on the internet or application platform of your wallet provider. Despite their ease of use, mobile and web wallets are the most susceptible to hackers and thieves who might get access to your phone’s passcode. If someone has access to your phone, they can send a “forgot password” message and receive a “change your password” code to login and send your bitcoins to their addresses.
Most cryptocurrency exchanges fall under web wallet classification. Most crypto exchanges are continually beefing up their security, but absolute protection remains difficult. As recently as a few days ago, there was a major cryptocurrency theft of $600m from Polynetwork.
You should always use 2 Factor Authentication or your fingerprint to get into your mobile or web wallet for added security. Mobile bitcoin wallet apps can be downloaded on your iOS App Store or Android Play Store.
Here are a few popular web and mobile wallets.
Desktop bitcoin wallets
Desktop bitcoin wallets are software programs you can download onto your laptop or computer. Desktop bitcoin wallets are more secure than mobile and web wallets. However, they also have their limitations with the security of the software program.
It is recommended to use a desktop wallet that encrypts your private key and account recovery phrases.
Here are some popular desktop bitcoin wallets;
Cold Bitcoin Wallets
Cold bitcoin wallets are hardware wallets. Hardware bitcoin wallets are physical storage devices for your bitcoin. Cold bitcoin wallets are offline hardware you can plug into your computer only when you need to receive or send bitcoins. They look similar to flash drives or external hard drives.
Hardware bitcoin wallets are the most secure way to store your bitcoins as they are much less susceptible to hacks or internet theft.
However, due to their nature, you must never lose your hardware wallet. If you do, your bitcoins are gone forever.
There are a few popular cold bitcoin wallets
Bitcoin Address
Your bitcoin wallet generates your bitcoin address. A bitcoin address is a code that acts as a source or destination for a bitcoin payment or transaction. Bitcoin wallets generate bitcoin addresses using cryptography. This cryptographic operation is done automatically when a transaction is initiated. It involves 3 steps.
- The wallet or software generates a private key through an asymmetric signature algorithm.
- The software derives the public key from the private key created in step 1.
- The user digitally signs with the private key and verifies that signature with the public key.
Unlike a digital wallet, a bitcoin address can not hold a balance. A bitcoin address is not meant to be permanent and it is recommended to generate a new address for each bitcoin transaction to make your transactions harder to trace.
Bitcoin Address Format
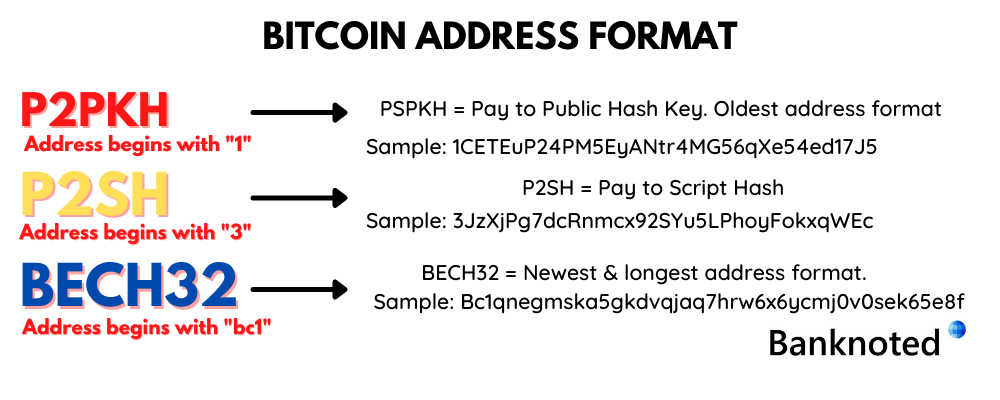
Bitcoin Addresses are 26 – 35 alpha-numeric (numbers and letters) characters. These bitcoin addresses begin with “1”, “3” or “bc1”. There are several bitcoin address formats today:
P2PKH (address starts with “1”)
P2PKH stands for Pay to Public Key Hash. This is the legacy or original bitcoin address format.
Example address: 1CETEuP24PM5EyANtr4MG56qXe54ed17J5
P2SH (address starts with “3”)
P2SH stands for Pay to Script Hash.
Example address: 3JzXjPg7dcRnmcx92SYu5LPhoyFokxqWEc
Bech32 (address starts with “bc1”)
Bech32 addresses are newer and longer in length than the other 2 formats. These addresses are fully compatible with SegWit.
Example address: Bc1qnegmska5gkdvqjaq7hrw6x6ycmj0v0sek65e8f
To learn more about bitcoin address formats, click here.
The Bitcoin Blockchain
 The bitcoin blockchain is a distributed public ledger. Think record book. This shared ledger maintains the history of all confirmed transactions on the bitcoin network. The software for the bitcoin blockchain is completely open-source. This means anyone can see and review the code. The blockchain is transparent and accessible to all users of the system. The blockchain helps every bitcoin wallet in the network know their available balance and how much each user can spend. The sequential order of transactions and the security of these transactions are protected by cryptography.
The bitcoin blockchain is a distributed public ledger. Think record book. This shared ledger maintains the history of all confirmed transactions on the bitcoin network. The software for the bitcoin blockchain is completely open-source. This means anyone can see and review the code. The blockchain is transparent and accessible to all users of the system. The blockchain helps every bitcoin wallet in the network know their available balance and how much each user can spend. The sequential order of transactions and the security of these transactions are protected by cryptography.
Bitcoin mining
 Bitcoins and the bitcoin network are secured by people called miners. Bitcoin miners verify all the transactions on the bitcoin network. You might be wondering why miners bother themselves with verifying transactions. Sounds boring and tedious. Yes, it is. However, miners are rewarded with newly created bitcoins for successfully verifying transactions. This is their incentive to keep the system running.
Bitcoins and the bitcoin network are secured by people called miners. Bitcoin miners verify all the transactions on the bitcoin network. You might be wondering why miners bother themselves with verifying transactions. Sounds boring and tedious. Yes, it is. However, miners are rewarded with newly created bitcoins for successfully verifying transactions. This is their incentive to keep the system running.
Bitcoin unconfirmed transactions
At any given time, there are thousands of unconfirmed transactions on the Bitcoin blockchain (bitcoin network). To check the status of your unconfirmed Bitcoin transaction, go here. You can search for your transaction using your wallet address or block hash.
Bitcoin whitepaper
The Bitcoin whitepaper is a 9 page document titled, “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.” It was written by Satoshi Nakamoto. It outlines how the bitcoin payments system works. Click here to read the original whitepaper.
Bitcoin official website
Bitcoin, itself, does not have an official website since it is an open source software with no central authority, however Bitcoin.org is an online resource dedicated to helping new Bitcoin users understand how it works. The domain was first registered to Satoshi Nakamoto before he left the project.
